TOLEDO, Ohio — When it rains, it pours! This week delivered more heavy downpours and severe thunderstorms that dumped several inches of rainfall on most of northwest Ohio and southeast Michigan. Heavy rain has been a recurring theme this summer, and flooding concerns have continually impacted the region.
In this week's edition of the Climate Friday Newsletter, Meteorologist John Burchfield will analyze the recent rainfall and discuss the link to climate change.
Two rounds of thunderstorms inundated the area on Wednesday, dumping up to 5 inches of rainfall on the area! The northern tier of Ohio and southern fringe of Michigan saw the heaviest rainfall, and locations from Cleveland to Toledo and Hillsdale picked up several inches of rainfall. Toledo officially recorded 2.23 inches of rain, raising the monthly total to 4.62 inches.
This July rainfall amount is now nearly two inches above-average. Locations like Dundee and Adrian also picked up nearly two and a half inches of rain. Isolated amounts of 4-5 inches impacted locations such as Hillsdale and Oregon. Flash flooding and wind damage impacted tens of thousands across the region as storms rolled through. These recent thunderstorms fit the wet theme of this month.


So what role does climate change play in torrential rainfall? First off, it's important to identify the effect of the weather pattern on daily and weekly fluctuations in the weather. This active storm track is in part caused by a high-pressure system stationed over the southern Great Plains. This high has delivered excessive heat across portions of the south and central United States, sending temperatures surging to the triple-digits.
This persistent high-pressure system and associated jet stream formation has dosed out frequent storm across the lower Great Lakes. Ohio and Michigan, on the periphery of the high, have seen an influx of weather disturbances along the jet stream. This weather pattern has delivered numerous storm systems, and has played a major role in this month's wet weather.
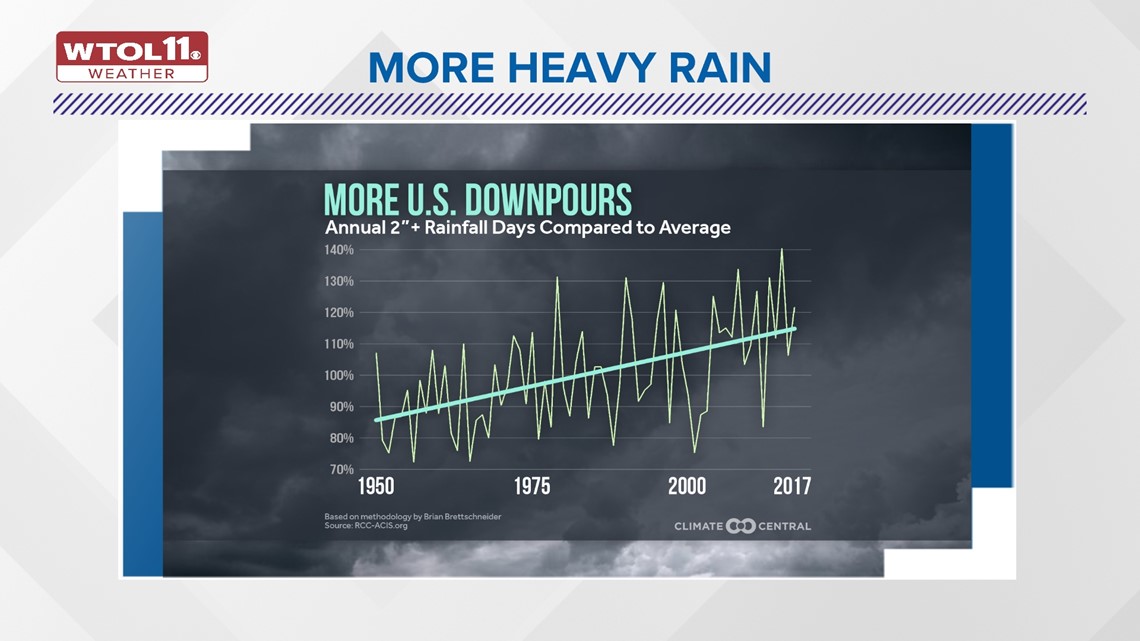
Though the weather pattern impacts daily and weekly fluctuations, climate change has caused more frequent flooding. With warmer temperatures across the globe, evaporation from lakes, oceans, and the soil has increased. With more moisture in the atmosphere, rainfall has become heavier. Mother Nature wrings out this moisture like a wash cloth, dumping heavy rain. Flooding downpours are more commonplace now than in past years, largely due to climate change.
Though the weather pattern has played a role in our active storm track, climate change is making heavy rainfall more intense. The wet weather pattern will finally shift toward a drier start to August, but the WTOL 11 weather team will update you on upcoming rain and storm chances.

More on WTOL: